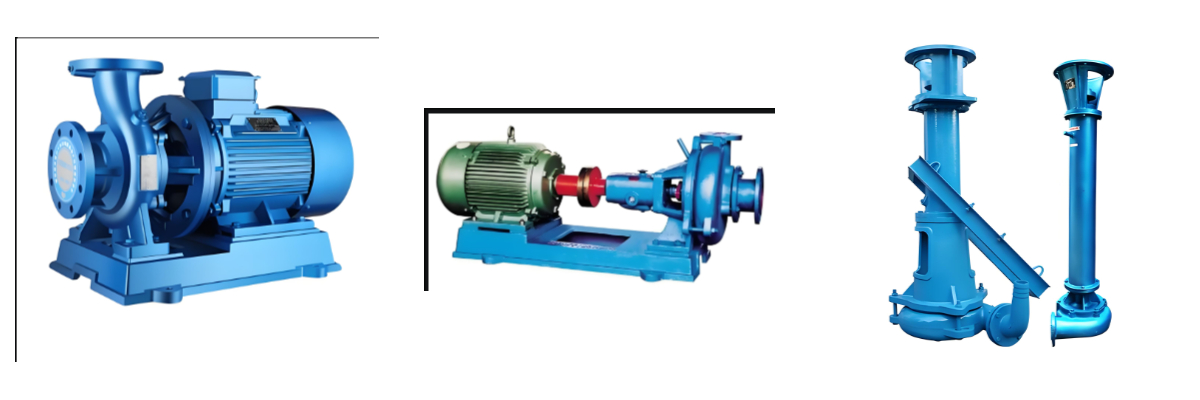
Centrifugal Mud Pump
Structure and maintenance
Compact structure, light weight, low manufacturing and installation costs, easy maintenance.
The use of corrosion-resistant materials can be applied to a variety of working conditions, and has strong self-priming ability.
Efficiency and applicability
High efficiency (up to 80%~95%), suitable for large flow and low head scenes, especially suitable for conveying normal temperature liquids (such as ethylene glycol, water, etc.).
Operation characteristics
The following is a detailed introduction to centrifugal mud pumps:
The motor drives the impeller to rotate. Under the action of centrifugal force, the mud is thrown from the center of the impeller to the outer edge to obtain energy, and leaves the outer edge of the impeller at high speed to enter the volute pump casing. In the volute, the mud slows down due to the expansion of the flow channel, and part of the kinetic energy is converted into static pressure energy, and finally flows into the discharge pipe at a higher pressure.
- Pump casing: Generally, a double-layer pump casing structure is adopted. The outer casing is mostly vertically open. The water outlet can be rotated to 8 different positions at 45° intervals, which is convenient for pipeline installation and layout.
- Impeller: It is a key component of the centrifugal mud pump. Its shape, size and material have an important influence on the performance and efficiency of the pump. It is mostly made of wear-resistant materials.
- Pump shaft: Connects the impeller and the motor, transmits power, and rotates the impeller. It must have sufficient strength and rigidity.
- Bearing: Used to support the pump shaft, reduce the rotational friction of the shaft, and ensure the stable rotation of the pump shaft.
- Sealing device: Prevent mud leakage. Common ones include auxiliary impeller shaft seal, packing shaft seal and mechanical seal.
- Flow rate: refers to the volume of mud delivered by the centrifugal mud pump per unit time, usually in cubic meters per hour (m³/h) or liters per second (L/s).
- Head: refers to the height to which the pump can lift the mud, in meters (m).
- Speed: the number of revolutions of the pump shaft per minute, in revolutions per minute (r/min).
- Power: includes shaft power and motor power. Shaft power is the power required by the pump when it is running, and motor power is the output power of the motor that drives the pump to run, both in kilowatts (kW).
- PN type centrifugal mud pump: single-stage, single-suction, horizontal structure, flow-through parts are made of wear-resistant alloy material, the gap between the impeller and the guard plate can be adjusted, and the shaft seal is a packing seal, which is suitable for conveying solid-liquid two-phase fluids in mining and other industries.
- GMZ centrifugal slurry pump: single-stage, single-suction, axial suction cantilever horizontal centrifugal pump, double pump casing structure, the impeller is equipped with back blades, and the shaft seal has three forms: auxiliary impeller shaft seal, packing shaft seal and mechanical seal.
- NL series centrifugal slurry pump: can handle viscous liquids, mud, sewage, etc., with large flow, suitable for river sewage cleaning, sewage treatment, farms, septic tanks and industrial wastewater.
Application areas
- Mining industry: used to transport slurry, tailings slurry, etc., and transport the slurry containing ore particles generated during the mining process to the designated location.
- Metallurgical industry: in the process of mineral processing, smelting, etc., centrifugal slurry pumps can be used to transport various slurries, waste slag slurries, etc.
- Power industry: used to transport fly ash slurry, desulfurization wastewater, etc., to treat and transport waste generated during coal-fired power generation.
- Environmental protection industry: can be used to transport sludge and sewage in sewage treatment plants, as well as transport mud and sediment in projects such as river dredging and lake dredging.