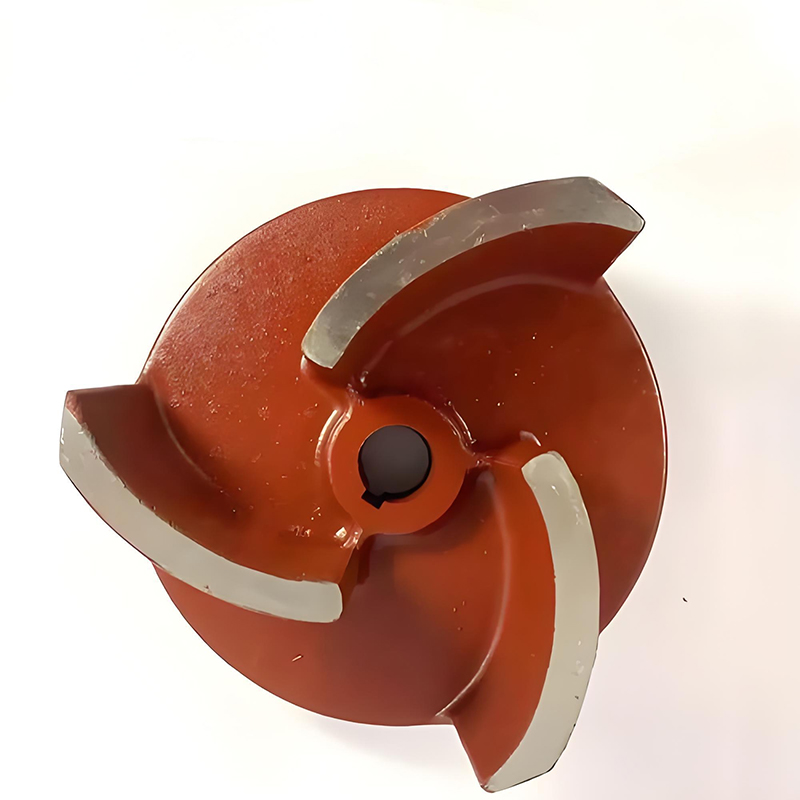
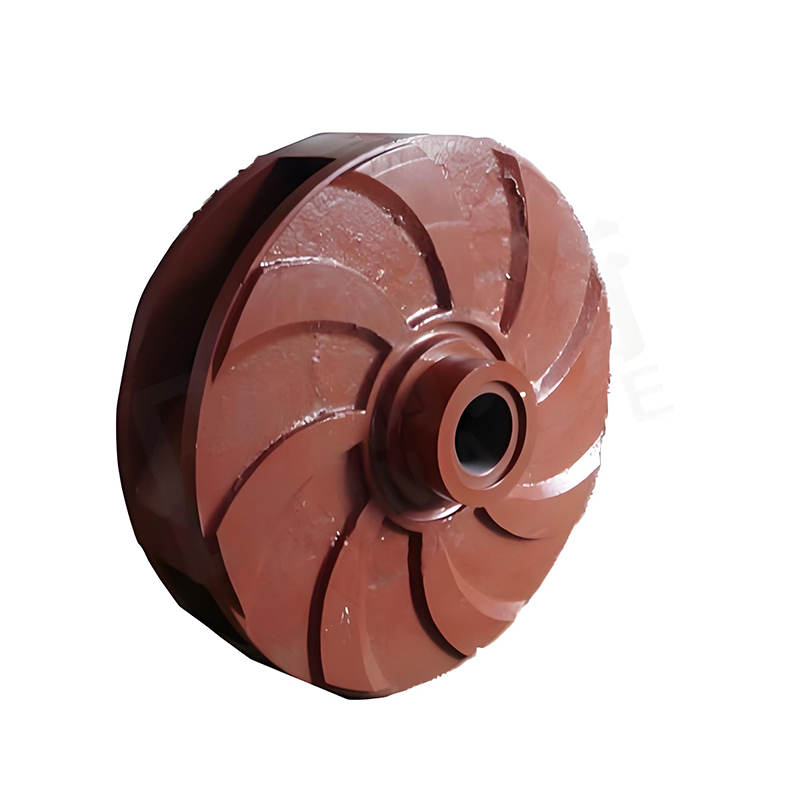
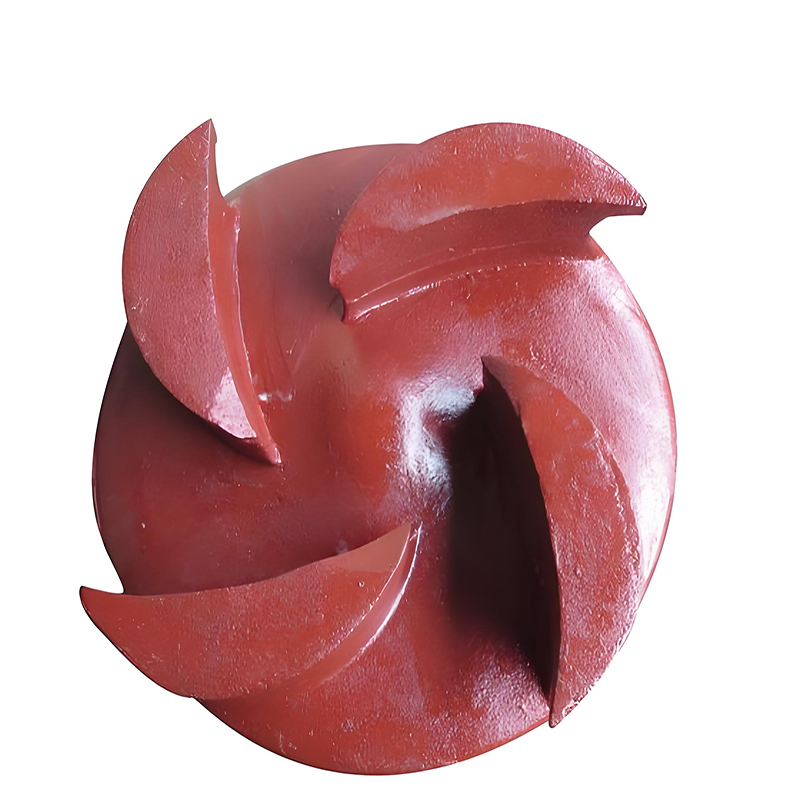
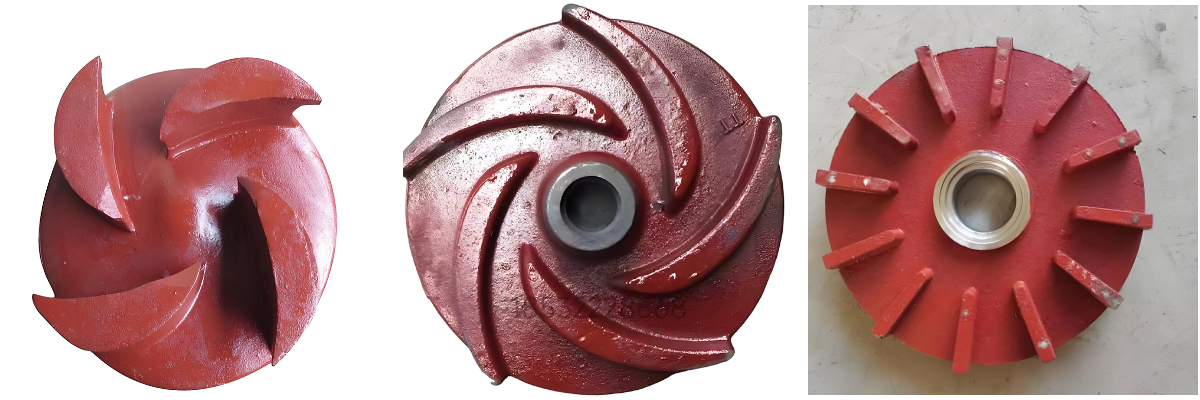
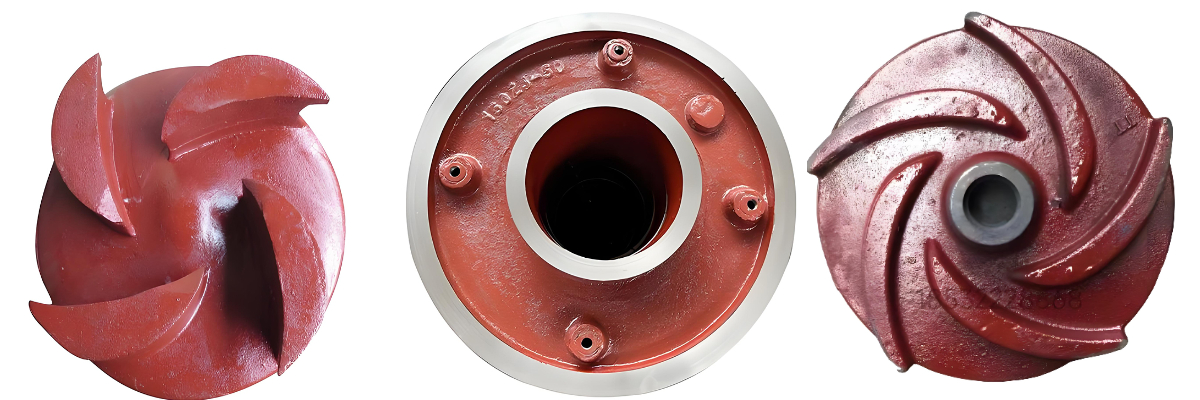
Impeller Slurry Pump
Selection of special materials: usually high chromium cast iron, wear-resistant rubber, wear-resistant ceramics and other materials are used. High chromium cast iron has high hardness (HRC55-65) and strong resistance to erosion and wear; rubber impellers are suitable for conveying corrosive or fine-grained slurry, with good elasticity and tear resistance; ceramic impellers have excellent wear resistance,
- Surface treatment enhancement: Some impellers will be heat treated (such as quenching) or sprayed with wear-resistant coatings (such as tungsten carbide) on the surface to further improve the wear life.
High chromium alloy: such as A05 (KmTBCr27), the heat treatment hardness can reach HRC58-62, with good abrasion resistance, suitable for strong abrasion conditions; A07 (KmTBCr15Mo3) has high hardness and strong wear resistance, and is used for high-concentration, high-lift and strong abrasive slurry transportation.
- Rubber: It has good elasticity and tear resistance, suitable for conveying corrosive or fine-particle slurry, which can reduce the wear of particles on the impeller, reduce noise and vibration.
- Polyurethane: Excellent wear resistance, high strength, good anti-aging performance, can maintain good performance in a wide temperature range, and can adapt to slurry transportation under different working conditions.
- Ceramics: extremely high hardness, excellent wear resistance, good chemical stability, can resist the erosion of high temperature, high concentration and strong corrosive slurry, but it is relatively brittle, and collision should be avoided during installation and use.
- Stainless steel: such as 2205 and other duplex stainless steel, with good corrosion resistance and certain wear resistance, suitable for conveying slurry containing corrosive media.
Structural form
- Closed impeller: There are covers on both sides, generally with 4-6 blades, mostly backward curved, high efficiency, suitable for conveying clean liquids without solid particles and fibers, single suction and double suction types.
- Open impeller: There are no front and rear covers, and the blades are connected to the hub through ribs. The structure is simple and easy to manufacture, but the efficiency is low. It is suitable for conveying slurries containing more solid suspended matter or fibers.
- Semi-open impeller: There is only a rear cover, suitable for conveying liquids that are easy to precipitate or contain solid suspended matter, and the efficiency is between open and closed impellers.
Working principle
When the motor drives the pump shaft to rotate, the impeller rotates accordingly, and the blades on the impeller generate thrust and pull on the liquid, causing the liquid to flow. Under the action of centrifugal force, the liquid is thrown from the center of the impeller to the outer edge and obtains energy, leaving the impeller and entering the volute. The liquid in the volute is decelerated by the gradual expansion of the flow channel, converting kinetic energy into static pressure energy, and finally flows into the discharge pipe at a higher pressure.